
Edit Content

Welcome to FabTrader Community!
Get in touch with me
hello@fabtrader.in


hello@fabtrader.in

For algo traders, automating trading strategies is essential for efficiency and execution speed. Zerodha offers an official trading API that allows users to programmatically place orders, fetch market data, manage portfolios, and more. However, Zerodha charges a fee for API access, which can be a barrier for many retail traders.
An alternative approach, commonly referred to as the ‘Token’ method, enables traders to execute transactions and retrieve data without using the official API. This method works by leveraging the session token that is generated when a user logs into the Zerodha Kite web platform. The idea is to extract and reuse this encrypted token in Python, making it appear as if trades are being placed manually through the web interface.
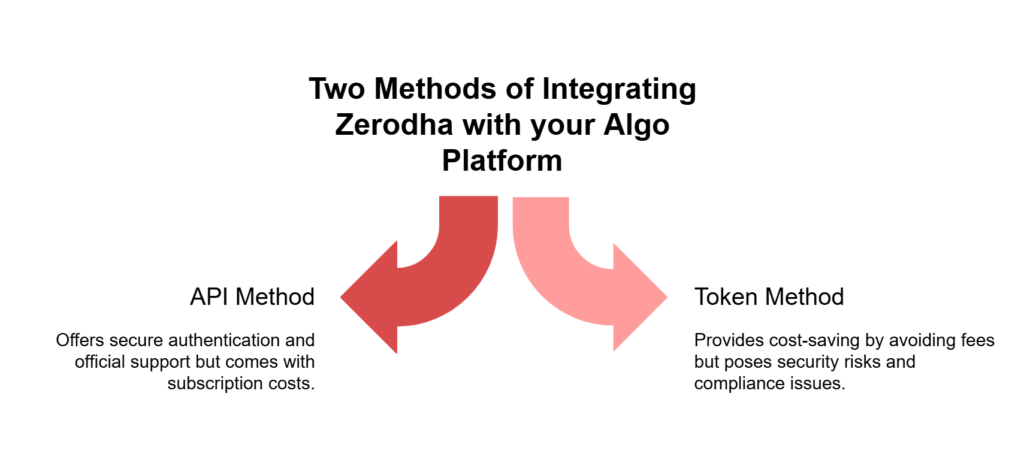
In this article, we will explore the technical workings of the Token method, explain how to implement it in Python, and discuss its advantages and limitations. We will also provide a Python script that automates the login process and demonstrates how to fetch user profile information using the encrypted token.
Unlike the API method, which requires an API key and OAuth authentication, the Token method works as follows:
enctoken).Since this method essentially emulates user actions from a browser, it does not require a paid API subscription. However, there are risks, such as token expiry and potential non-compliance with Zerodha’s terms of service.
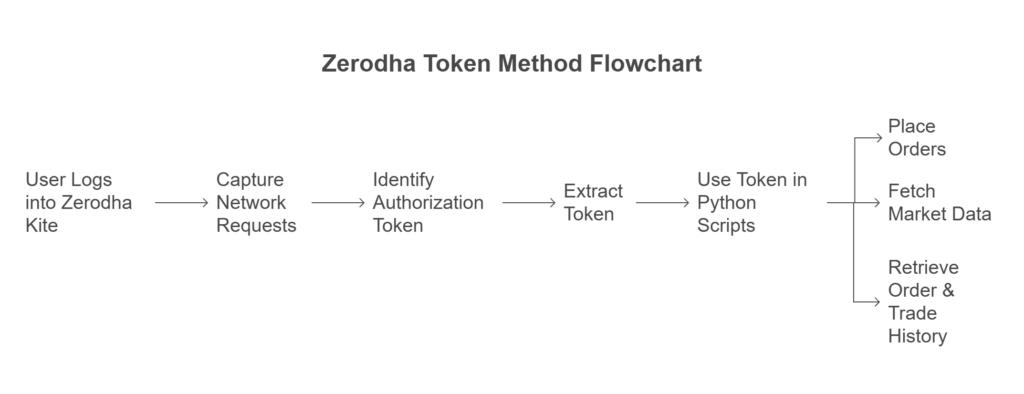
The following Python script automates the Zerodha login process and extracts the encrypted token for further use.
Before running the script, ensure you have the required Python modules installed. You can install them using:
pip install requests pyotp
import pyotp
import requests
# Your Credentials
user_id = 'your userid'
password = 'your password'
totp_key = 'your totp key'
# Initial Login (to get request_id from Zerodha
session = requests.Session()
login_response = session.post(
'https://kite.zerodha.com/api/login', data={
"user_id": user_id,
"password": password
})
# Generate and capture Encrypted Token from Zerodha
two_fa = pyotp.TOTP(totp_key).now()
twofa_response = session.post(
'https://kite.zerodha.com/api/twofa',
data={
"request_id": login_response.json()['data']['request_id'],
"twofa_value": two_fa,
"user_id": login_response.json()['data']['user_id']
})
enctoken = twofa_response.cookies.get('enctoken')
print("Encrypted Token : ", enctoken)
# Sample usage of Encrypted Token to get the user's profile
def profile():
root_url = "https://kite.zerodha.com/oms"
headers = {"Authorization": f"enctoken {enctoken}"}
profile = session.get(f"{root_url}/user/profile", headers=headers).json()["data"]
return profile
print(profile())https://kite.zerodha.com/api/login with the user ID and password.request_id that is required for 2FA authentication.pyotp library.request_id, is submitted to https://kite.zerodha.com/api/twofa.enctoken), which is stored in cookies.https://kite.zerodha.com/oms/user/profile, using the enctoken in the request header.Once you have the enctoken, you can perform various actions on Zerodha, including:
https://kite.zerodha.com/oms/ordershttps://kite.zerodha.com/oms/portfolio/positionshttps://kite.zerodha.com/oms/orders/regularhttps://kite.zerodha.com/oms/orders/{order_id}To interact with these endpoints, simply include the enctoken in the request headers as shown in the profile-fetching function.
The following python code contains the full python implementation of all functions/methods listed above. You can copy this code into your source folder and import it where required and simply call the functions listed here!. Its that simple…
import os
try:
import requests
except ImportError:
os.system('python -m pip install requests')
try:
import dateutil
except ImportError:
os.system('python -m pip install python-dateutil')
import datetime as dt
import requests
import dateutil.parser
def get_enctoken(userid, password, twofa):
session = requests.Session()
response = session.post('https://kite.zerodha.com/api/login', data={
"user_id": userid,
"password": password
})
response = session.post('https://kite.zerodha.com/api/twofa', data={
"request_id": response.json()['data']['request_id'],
"twofa_value": twofa,
"user_id": response.json()['data']['user_id']
})
enctoken = response.cookies.get('enctoken')
if enctoken:
return enctoken
else:
raise Exception("Enter valid details !!!!")
class KiteApp:
# Products
PRODUCT_MIS = "MIS"
PRODUCT_CNC = "CNC"
PRODUCT_NRML = "NRML"
PRODUCT_CO = "CO"
# Order types
ORDER_TYPE_MARKET = "MARKET"
ORDER_TYPE_LIMIT = "LIMIT"
ORDER_TYPE_SLM = "SL-M"
ORDER_TYPE_SL = "SL"
# Varities
VARIETY_REGULAR = "regular"
VARIETY_CO = "co"
VARIETY_AMO = "amo"
# Transaction type
TRANSACTION_TYPE_BUY = "BUY"
TRANSACTION_TYPE_SELL = "SELL"
# Validity
VALIDITY_DAY = "DAY"
VALIDITY_IOC = "IOC"
# Exchanges
EXCHANGE_NSE = "NSE"
EXCHANGE_BSE = "BSE"
EXCHANGE_NFO = "NFO"
EXCHANGE_CDS = "CDS"
EXCHANGE_BFO = "BFO"
EXCHANGE_MCX = "MCX"
def __init__(self, enctoken):
self.enctoken = enctoken
self.headers = {"Authorization": f"enctoken {self.enctoken}"}
self.session = requests.session()
self.root_url = "https://kite.zerodha.com/oms"
self.session.get(self.root_url, headers=self.headers)
def instruments(self, exchange=None):
data = self.session.get(f"https://api.kite.trade/instruments").text.split("\n")
Exchange = []
for i in data[1:-1]:
row = i.split(",")
if exchange is None or exchange == row[11]:
Exchange.append({'instrument_token': int(row[0]), 'exchange_token': row[1], 'tradingsymbol': row[2],
'name': row[3][1:-1], 'last_price': float(row[4]),
'expiry': dateutil.parser.parse(row[5]).date() if row[5] != "" else None,
'strike': float(row[6]), 'tick_size': float(row[7]), 'lot_size': int(row[8]),
'instrument_type': row[9], 'segment': row[10],
'exchange': row[11]})
return Exchange
def historical_data(self, instrument_token, from_date, to_date, interval, continuous=False, oi=False):
params = {"from": from_date,
"to": to_date,
"interval": interval,
"continuous": 1 if continuous else 0,
"oi": 1 if oi else 0}
lst = self.session.get(
f"{self.root_url}/instruments/historical/{instrument_token}/{interval}", params=params,
headers=self.headers).json()["data"]["candles"]
records = []
for i in lst:
record = {"date": dateutil.parser.parse(i[0]), "open": i[1], "high": i[2], "low": i[3],
"close": i[4], "volume": i[5],}
if len(i) == 7:
record["oi"] = i[6]
records.append(record)
return records
def quote(self, instrument_token):
try:
from_date = dt.date.today() - dt.timedelta(days=5)
to_date = dt.date.today()
interval = "day"
params = {"from": from_date,
"to": to_date,
"interval": interval,
"continuous": 0,
"oi": 0}
lst = self.session.get(
f"{self.root_url}/instruments/historical/{instrument_token}/{interval}", params=params,
headers=self.headers).json()["data"]["candles"]
record = {}
for i in lst:
record = {"date": dateutil.parser.parse(i[0]), "open": i[1], "high": i[2], "low": i[3],
"close": i[4], "volume": i[5], }
return record
except:
return None
def ltp(self, instrument_token):
ltp = None
try:
from_date = dt.date.today() - dt.timedelta(days=5)
to_date = dt.date.today()
interval = "day"
params = {"from": from_date,
"to": to_date,
"interval": interval,
"continuous": 0,
"oi": 0}
lst = self.session.get(
f"{self.root_url}/instruments/historical/{instrument_token}/{interval}", params=params,
headers=self.headers).json()["data"]["candles"]
if len(lst) != 0:
for i in lst:
ltp = i[4]
return ltp
except:
return ltp
def margins(self):
margins = self.session.get(f"{self.root_url}/user/margins", headers=self.headers).json()["data"]
return margins
def profile(self):
profile = self.session.get(f"{self.root_url}/user/profile", headers=self.headers).json()["data"]
return profile
def orders(self):
orders = self.session.get(f"{self.root_url}/orders", headers=self.headers).json()["data"]
return orders
def positions(self):
positions = self.session.get(f"{self.root_url}/portfolio/positions", headers=self.headers).json()["data"]
return positions
def place_order(self, variety, exchange, tradingsymbol, transaction_type, quantity, product, order_type, price=None,
validity=None, disclosed_quantity=None, trigger_price=None, squareoff=None, stoploss=None,
trailing_stoploss=None, tag=None):
params = locals()
del params["self"]
for k in list(params.keys()):
if params[k] is None:
del params[k]
order_id = self.session.post(f"{self.root_url}/orders/{variety}",
data=params, headers=self.headers)
return order_id
def modify_order(self, variety, order_id, parent_order_id=None, quantity=None, price=None, order_type=None,
trigger_price=None, validity=None, disclosed_quantity=None):
params = locals()
del params["self"]
for k in list(params.keys()):
if params[k] is None:
del params[k]
order_id = self.session.put(f"{self.root_url}/orders/{variety}/{order_id}",
data=params, headers=self.headers).json()["data"][
"order_id"]
return order_id
def cancel_order(self, variety, order_id, parent_order_id=None):
order_id = self.session.delete(f"{self.root_url}/orders/{variety}/{order_id}",
data={"parent_order_id": parent_order_id} if parent_order_id else {},
headers=self.headers).json()["data"]["order_id"]
return order_idenctoken expires after a session timeout or logout. Usually valid only for less than 24 hours. While using this method, you will not be able to use the Zerodha Kite terminal on a desktop. However, you can still use it via Mobile. 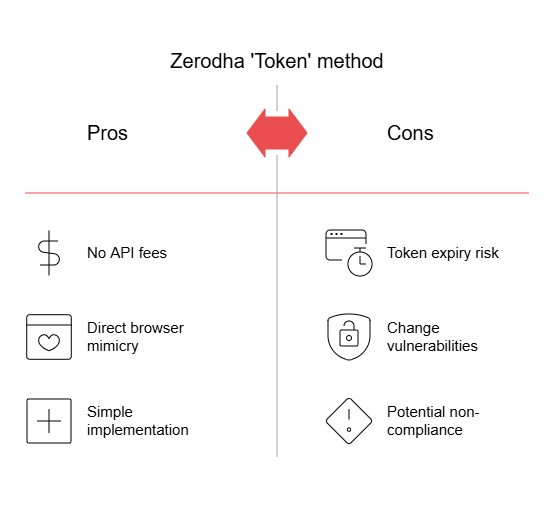
The Token method provides a workaround to Zerodha’s API fees by mimicking browser requests and reusing an encrypted session token. While it allows algo traders to automate order placements and fetch trading data for free, it comes with certain risks, such as token expiration and compliance concerns.
If you’re considering using this approach, ensure you understand the potential risks and take necessary precautions. Happy Trading! 🚀
Support this community : FabTrader.in is a one-person initiative dedicated to helping individuals on their F.I.R.E. journey. Running and maintaining this community takes time, effort, and resources. If you’ve found value in the content, consider making a donation to support this mission.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for educational and informational purposes only and should not be construed as financial, investment, or legal advice. The content is based on publicly available information and personal opinions and may not be suitable for all investors. Investing involves risks, including the loss of principal. Always conduct your own research and consult a qualified financial advisor before making any investment decisions. The author and website assume no liability for any financial losses or decisions made based on the information presented.
Vivek is an algorithmic trader, Python programmer, and a passionate advocate of the F.I.R.E. (Financial Independence, Retire Early) movement. He achieved his financial independence at the age of 45 and is dedicated to helping others embark on their own journeys toward financial freedom.
©2024 Fabtrader.in - An unit of Rough Sketch Company. All Rights Reserved